Laser technology has become a widespread method for creating durable marks or patterns on materials. In this field, laser marking and laser engraving are two standard methods. They play an essential role in many different applications. For industrial manufacturing or personal customization, laser marking and engraving provide precise, efficient, and durable marking solutions.
Both techniques involve processing materials with laser beams. However, there are some excellent differences in their working principles, application scope, and effects. This article will explore the two methods of laser marking and engraving. It is intended to help readers understand their respective characteristics, advantages, and limitations. To help you make wise choices in specific situations. You may be a manufacturer considering how to add markings to a product or an artist trying to leave a timeless mark on a material. This article will highlight the critical factors in deciding between laser marking and engraving.
Laser Marking Overview
Laser marking is a method of creating permanent marks on various materials. This method is highly accurate and efficient. It uses a focused laser beam to modify the surface of a material, creating a contrast that makes the desired mark or pattern. Unlike traditional printing or mechanical engraving methods, laser marking does not involve direct contact with the material. It eliminates the risk of abrasion.
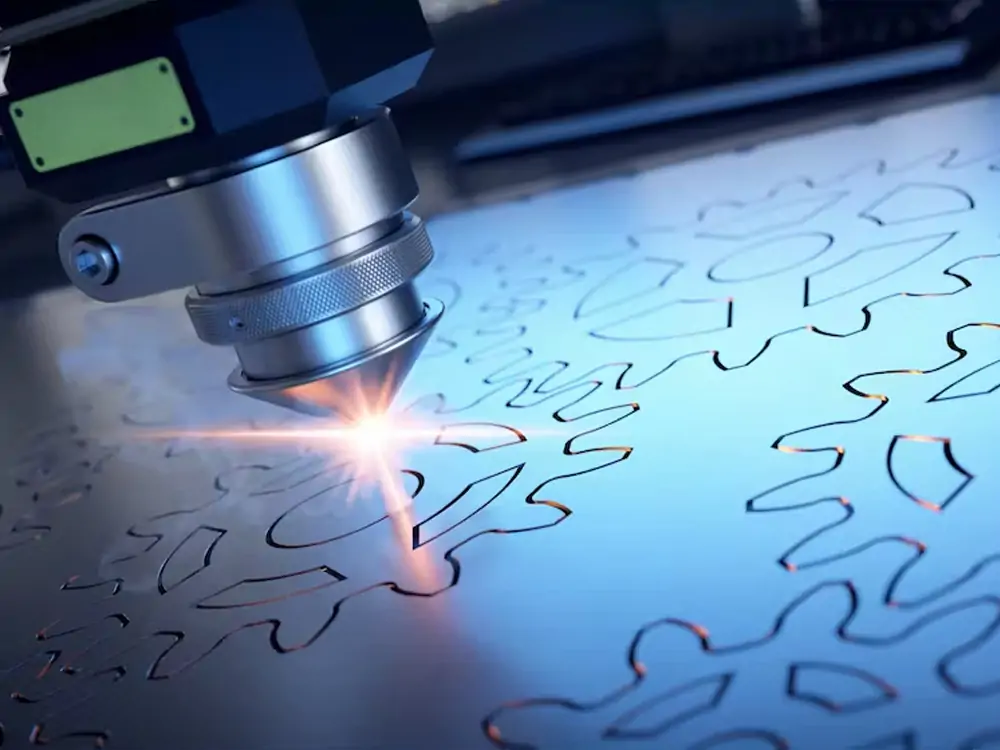

Laser Marking Process
- Laser Etching: Removes a thin layer of material from a surface, creating a slightly recessed mark. Laser etching often adds serial numbers, barcodes, and other identifying information to products.
- Laser Annealing: A laser beam heats the surface of a material to cause oxidation or color changes. It creates a permanent, visually unique mark. This will not compromise the integrity of the material. Laser annealing is commonly used on metals and plastics.
- Laser Foaming: This method is mainly used for plastics. Raised markings are produced by heating a material’s surface to expand and form a foam-like texture.
- Color Change Marking: Lasers can make visible color changes by changing the pigments or dyes present in the material. This technique is commonly used with plastics. It is famous for aesthetic or branding purposes.
Advantages of Laser Marking
Laser marking is a versatile and efficient technology. It is used to create permanent marks or designs on various materials. It offers several advantages over traditional marking methods. Such as engraving, printing, or mechanical. Some of the key benefits of laser marking include the following.
Precision And Accuracy
Laser marking technology offers exceptional precision and accuracy. It can create intricate and detailed marks, even on small or delicate objects. It is beneficial for applications requiring high precision. Examples include medical devices or aerospace components.
Non-contact Process
Laser marking is a non-contact process. This means no physical contact exists between the laser beam and the material being marked. It eliminates the risk of material damage or surface deformation. Therefore, it is more suitable for delicate items.
Permanent Marker
Laser marking is highly durable and resistant to abrasion and fading. It makes laser marking ideal where durable identification is required.
Broad Material Compatibility
Laser marking can be performed on a wide variety of materials. These include metal, plastic, ceramic, glass, rubber, and wood. It can adjust the parameters of the laser to suit the specific material, ensuring the best results.
Flexibility And Customization
Laser marking offers excellent flexibility in design and customization. Intricate designs, barcodes, serial numbers, logos, and text can be easily marked on surfaces. So it can meet specific branding or identification requirements.
Minimal Material Removal
Laser marking involves minimal material removal. It is unlike traditional engraving methods that remove material from the surface. It is beneficial for maintaining the structural integrity and appearance of the marked object.
Reduce Maintenance
Laser marking systems typically have fewer moving parts than mechanical marking methods. This reduces maintenance requirements and increases service life.
Environmental Friendly
Laser marking is considered an environmentally friendly process. Because it does not involve the use of inks, chemicals, or solvents that can create waste or harmful emissions.
Automation And Integration
Laser marking systems can be easily integrated into automated production lines. It thus enables a seamless and efficient marking process. This integration helps improve workflow and reduce labor costs.
Disadvantages of Laser Marking
- Material Limitations: Laser marking is suitable for many materials. Such as metal, plastic, and ceramic. However, some materials may need to be more ideal for laser processing. Damaged, discolored, or deformed as they may absorb laser energy.
- High Cost: Laser marking equipment itself and maintenance costs are high. Purchasing, installing, and maintaining laser equipment can burden some small and medium-sized businesses.
- Safety Concerns: The powerful beams produced by laser systems can cause damage to human eyes and skin. Appropriate security measures must be taken. Such as wearing proper protective glasses to prevent laser radiation injury.
Applications of Laser Marking
Laser marking has many advantages. Therefore, it has been widely used in many application fields. Below are some examples of areas of application for laser marking.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Laser marking can mark serial numbers, barcodes, dates, and production batches. It can also mark other parts, products, and tools information. It can also brand metal, plastic, ceramic, and other materials.
- Auto Industry: Laser marking can be used for marking automotive parts. For traceability, identification, and anti-counterfeiting, such as engine parts, chassis components, glass, etc.
- Electronics Industry: Laser marking can make tiny marks on the surface of electronic components, chips, and circuit boards. It is for identification, tracking, and anti-counterfeiting.
- Medical Instruments: Laser marking can mark medical devices, organ transplants, and other medical applications. It can ensure product traceability and quality.
- Aerospace: In aerospace, laser marking can mark plane parts and spacecraft components. It is for identification and traceability.
- Jewelry And Accessories: Laser marking can make fine marks on jewelry, watches, glasses, and other items. It can be for brand identification and anti-counterfeiting.
- Food Packaging: Laser marking can mark information on food packaging. Such as production date and shelf life. It can ensure food safety and compliance.
- Building Materials: Laser marking can be used on construction materials. Such as concrete and stone to mark the manufacturer, batch, and other information.
- Home Appliance Manufacturing: Laser marking can be used to identify brand, model, and technical specifications on products. Such as household appliances and kitchen equipment.
- Arts And Creative Fields: Laser marking can also be used for creative marking on artwork and handmade products. It gives the work a unique identity.
Laser Engraving Overview
Laser engraving is a precise and versatile technique. It uses a focused laser beam to remove material from the surface of an object. So it can create a permanent mark, design, or pattern. Traditional engraving methods involve physical contact with the material. At the same time, laser engraving is a non-contact process. It is, therefore, suitable for a wide range of materials and applications.
How Laser Engraving Works
- Laser Source: A laser engraver uses a high-energy laser beam produced by a laser source. The most common types of lasers used for engraving are CO2 lasers and fiber lasers. CO2 lasers are commonly used on organic materials such as wood, acrylic, and fabric. Fiber lasers are better suited for metals and plastics.
- Focusing Optics: The laser beam passes through a series of lenses and mirrors that concentrate it into a small but strong point called a focal point. This concentrated energy enables precise engraving.
- Material Interaction: When a focused laser beam interacts with a material surface. It heats the material to vaporization or melting. This process removes a small amount of material, leaving the desired engraving.
- Computer Control: The whole process is controlled by a computer system. The system interprets digital design files and guides a laser head over the material.
Applications of Laser Engraving
- Personalization And Customization: Laser engraving personalizes jewelry, gifts, trophies, and accessories. Names, logos, dates, and intricate designs can be engraved on various surfaces.
- Product Branding And Identification: Manufacturers use laser engraving to add logos, serial numbers, batch codes, and other identifying information to their products. It facilitates traceability and anti-counterfeiting measures.
- Signage And Advertising: Laser engraved signage, plaques, and promotional materials are standard at businesses and events. The high precision of laser engraving enables detailed designs and beautiful text.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers use laser engraving to create intricate patterns, relief art, and sculptures on various materials. The precision and repeatability of the process make it a favorite in the creative world.
- Electronic And Medical Equipment: Laser engraving marks components, serial numbers, and technical information on many equipment. Including electronic equipment, medical devices, and surgical implants.
- Aerospace And Automotive: Key components in the aerospace and automotive industries are often laser engraved. They are for identification, tracking, and quality control.
- Woodworking And Crafts: Woodworking uses laser engraving to create detailed designs, textures, and inlays in wood. Artisans also use it on leather, paper, fabric, and other materials.
- Architectural Models: Laser-engraved architectural models showcase intricate details and textures in miniature structures.
Advantages of Laser Engraving
- High precision and accuracy.
- The non-contact process reduces the risk of material damage.
- Wide range of compatible materials. From metal to plastic, wood, glass, and more.
- Versatility for a variety of applications from industrial to artistic.
- The process is efficient and fast, suitable for small-scale and large-scale production.
- Minimal maintenance compared to traditional engraving methods.
Disadvantages of Laser Engraving
- Limited Materials: Laser engraving works best on certain materials. Such as wood, acrylic, glass, and metal. However, certain materials may not respond well to laser engraving. Such as reflective surfaces, transparent materials, and plastics.
- Depth Limitations: It is capable of creating detailed surface patterns. Laser engraving may not be suitable for deep engravings.
Conclusion
We have compared the two advanced processing technologies of laser marking and engraving. We also discussed their technical details. We thought about their unlimited potential in different application fields. They have features of high-precision, high-efficiency, and non-contact processing characteristics. So, they have profoundly affected industry, medical treatment, and art.
Laser marking is a rapid and precise marking method. It has significant advantages in the pursuit of product personalization and traceability. However, it may be limited in some applications and more sensitive to material damage. In contrast, laser engraving, although relatively long in processing time. But it can achieve deeper, longer-lasting markings. Laser engraving is more attractive where resistance to wear and environmental influences is required.
Comprehensive consideration, whether to choose laser marking or laser engraving, depends on your specific needs and application scenarios. Laser technology is a compelling solution whether looking for speed and precision in marking or profound and durable results.
