Laser welding is a popular method of joining metal parts nowadays. People often wonder about its thickness capacity. How thick can a handheld laser welder weld? What are the requirements? How deep can it melt the mating surfaces? All these questions arise, especially when you intend to choose laser welding for your work.
As you know, the appropriate joint thickness creates strong bonds while stopping the formation of defects. Different materials need different thickness settings. For example, aluminum and stainless steel need special care during welding.
Hand-held laser welders are more popular than automated ones in laser welding. These machines are incredibly lightweight, easy to carry, and offer accurate welding.
This article discusses the thickness capabilities of a hand-held laser welder. You will learn which laser power can weld and how thick the metals are. Also, you will know when you should use the wire feeder. Ultimately, you will determine what factors to consider during laser welding.
How Thick Can a Handheld Laser Welder Weld?
A hand-held laser welder can typically work with various metals. Since it is versatile, people often choose this device for various metal fabrication works. However, you must know how each metal behaves with a laser to get the best results.
For instance, aluminum is quite tricky to weld. There are two reasons for this: reflectivity and thermal conductivity. On the other hand, stainless steel has a very high melting point. Naturally, it needs high laser power, but it is not. Stainless steel has an excellent thermal absorption capability. Thus, it can offer you a robust weld result.
Therefore, the thicker metals you work with, the more laser power you need. Some metals may expand due to heat absorption and create distorted shapes. Coated or dirty surfaces may also interfere with the welding quality.
Laser Welding Stainless Steel
As usual, a portable laser welder allows you to handle various stainless steel thicknesses. Still, you have to concentrate on the suitable laser settings. One 1000W laser welder, for instance, can weld stainless steel up to 6mm thick. A 1500W laser may, therefore, accomplish up to 7mm, 2000W up to 8mm, and 3000W up to 9mm consecutively.
Their depth of melting is what? Up to 2mm of stainless steel may be melted using a 1000W portable laser welder. A 1500W may consecutively reach 2.8mm, 2000W up to 3.2mm, 3000W up to 4.5 mm. On stainless steel, every laser power has a different thickness capacity.
Regarding welding speed, the more laser power you have, the quicker you can weld. Assume, for instance, that you are handling a 1mm stainless steel sheet. A 1000W laser welder can weld at 30mm/s, 1500W at 40mm/s, 2000W at 55mm/s, and 3000W at 80mm/s.

Laser Welding Aluminum
Aluminum is another popular metal widely used in laser welding. Similar to stainless steel, aluminum thicknesses also vary with the laser power. Starting with 1000W, it works up to 2.5mm thick aluminum and can melt up to 1mm deep. On the other hand, 1500W can reach up to 3mm thick aluminum and melt 1.8mm deep. You could use these hand-held laser welders for small—to medium-sized work.
However, you must add more laser powers if you want more capabilities. A 2000W laser welding machine can weld up to 4.5mm aluminum, melting to 2.0mm deep. On the other hand, a 3000W and held laser welder welds up to 5mm thick, which can melt up to 3mm deep.
If you use a 1mm thick aluminum, a 1000W hand-held laser welder can weld at 20mm/s. Consecutively, a 1500W laser welder can weld at 25mm/s, a 2000W laser welder at 55mm/s, and a 3000W laser welder at 75mm/s.
You may wonder why aluminum, a soft metal, needs this much power. Compared to stainless steel, you can work with less thick aluminum. There are two reasons behind this. First, aluminum reflects the laser beam, which makes it difficult to melt it. Second, aluminum has high thermal conductivity. This means it can quickly dissipate heat. Therefore, the speed required is also comparatively slower than that of stainless steel.
Laser Welding Brass
Similar to aluminum, brass is also reflective and heat-conductive. The hand-held laser welders mentioned above can weld brass from 3mm to 5mm thick.
Although brass requires higher laser power, it requires special care during welding. Inappropriate laser settings can quickly cause distortion or deformation. However, laser-welding brass is used in jewelry, electronics, and other industries.
Laser Welding Copper
Hand-held laser welders with 3000W power can weld up to a thickness of 4mm copper. There are high-power welders as well, which can work at 5mm. Low-power welders, like 1000W welders, work on 1mm thick copper.
Laser welding copper is much more efficient and precise than traditional welding. For better results, you can choose pulsed lasers. You could also use shielding gas for a better and cleaner weld.
When to Use or Not to Use Wire Feeder for Laser Welding?
It is tricky to understand when and not to use the wire feeder. Most beginners make mistakes here. Although they use a high-power laser, they do not get the desired weld strength.
When to Use
A wire feeder should be used when the weld is more than 0.3 mm.
If a joint face gap exists, a wire feeder helps bridge and fuse them. Adding filler wire to modify a weld’s strength and hardness properties can improve its mechanical character. A filler wire can enhance penetration and improve welding quality in deeper welding.
When not to use
On the contrary, if a metal sheet is less than 1 mm thick, the worker should not use a wire feeder for welding.
A filler wire may cause excessive heat input and distortion when welding thin materials. It is also unnecessary when the base material has good fusion properties with decent gaps. During high-speed automated welding, a feeder adds perplexities and requires maintenance. Moreover, wire feeding can slow down the welding process compared to autogenous laser welding.
What Should You Pay Attention When Using a Handheld Laser Welding Machine?
Laser welding is excellent for precision welding. It is true. However, things may get messy if you don’t follow some precautions. Below are some critical factors you must pay attention to during laser welding.
#1 Laser Power Selection
The most critical step for laser welding is choosing the appropriate laser power. As you know, the exact laser power depends on specific types of metals. If you are working with thin metal parts, a 1000W laser welder could do an excellent job. For moderate thickness, you could opt for a 2000W laser welder. For thicker metals, you could choose 3000W.
#2 Process Parameters
The perfect laser welding is not limited to choosing the appropriate laser power. You must also focus on adjusting the correct laser parameter settings. Slow welding may create high heat input and distortion or high HAZ. On the other hand, quicker welding may produce incomplete work.
#3 Safety Measures
You should also ensure your safety before welding the metals. Always use goggles rated for the specific laser wavelength. Protective equipment like gloves, long sleeves, and aprons should be used to avoid high HAZ. Make sure there is good airflow to remove harmful fumes. Never look directly at the laser beam or point at reflective surfaces.
#4 HAZ Control
Appropriate power and speed settings will decrease the heat-affected zone (HAZ). Few materials, such as high-carbon steels, benefit from preheating to restrain cracking. Each material should achieve room temperature during every pass to prevent excessive heat accumulation.
#5 Wire Feeder Use
In some cases, the wire feeder plays a vital role in welding. If joint fit-up is imperfect, you can bridge the gaps with a wire feeder. It increases the mechanical strength of welding. Also, it prevents cracking down as well.
Position the wire properly at a 30°–45° angle for smooth feeding into the molten pool. Finally, the wire feed rate must match the welding speed to prevent the weld from overfilling or underfilling.
You know all the precautions and steps before using a handheld laser welder. You must follow these steps for the best outcome and safety.

Hand-held Laser Welding VS Other Methods: Thickness Capabilities
A handheld laser welder offers accurate, quick, and high-quality welding. It usually comes in various laser powers ranging from 1000W to 3000W. It can weld various metals from 1mm to 9mm. Although it can’t offer high welding thickness, it is accurate and offers more robust joints. Because of this, hand-held laser welders are superior to traditional TIG or MIG.
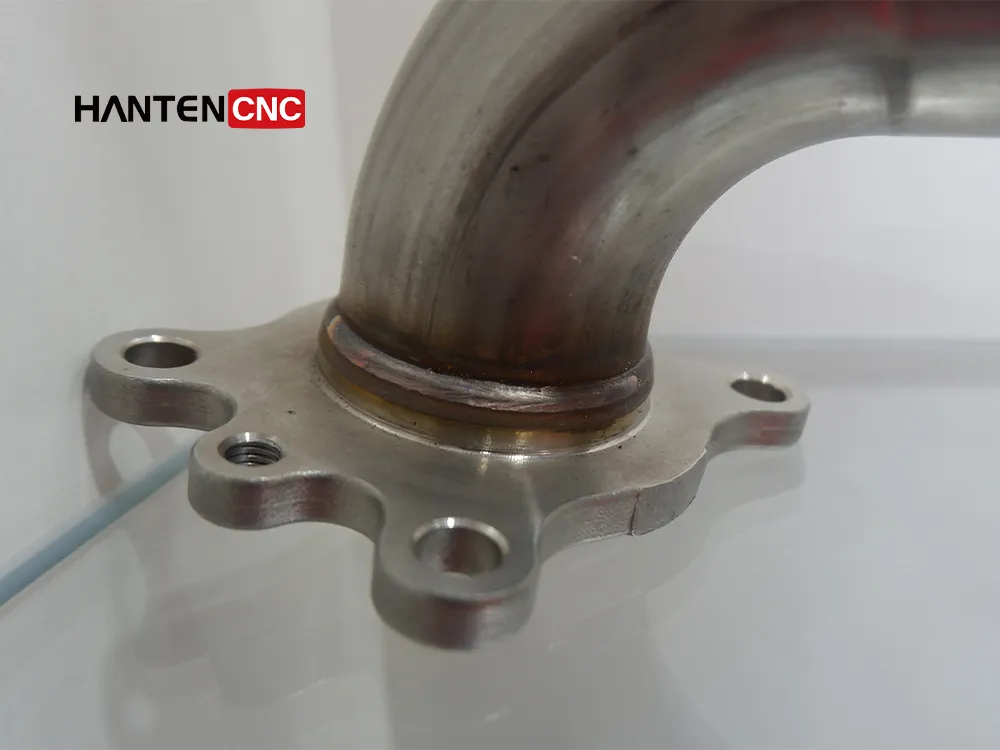

On the other hand, traditional methods, like TIG, MIG, or plasma welding, can weld even thicker metals. MIG can handle thicknesses beyond 10mm, while stick welding can handle up to 12mm thick metals. The exact weld thickness typically depends on power settings and welding techniques. Plasma welding can produce more heat input. Thus, you can weld thicker metals with this technique.
However, all these techniques cannot offer a high-quality weld with less HAZ. Only laser welding can provide such an outcome.
Contact Us Today!
Contact us today if you are looking for reliable hand-held laser welding solutions. Hanten CNC produces high-quality laser welders, both hand-held and automated. If you are interested, please navigate to our laser welding collections. For more information, reach out to our customer support team.
